Archive for March 2025
Personality perspective on depression and anxiety symptoms among Chinese adolescents and young adults: a two-sample network analysis
Can the UK fix its broken prison system?
Estimating Different Value Functions of the Prospect Theory According to Individual Decision‐Making Styles
“In Weapons We Trust?” Four-culture analysis of factors associated with weapon tolerance in young males
The Cycle of Violence: Childhood Abuse, Illicit Drug Use and Adult Intimate Partner Violence Perpetration
Comparing Equivalence‐Based Instruction to a PowerPoint Video Lecture to Teach Differential Reinforcement Descriptors to College Students
The stickiness of unequal housework sharing: Limited effects of couples’ ideological pairings
The Effect of a Multi-modal Program on Fear of Cancer Recurrence in Breast Cancer Patients
Millions to Lose Health Coverage if ACA Tax Credits End
Unattractive, corrupted, and culpable feared self-themes: Expanding our understanding of self-concept in relation to eating pathology
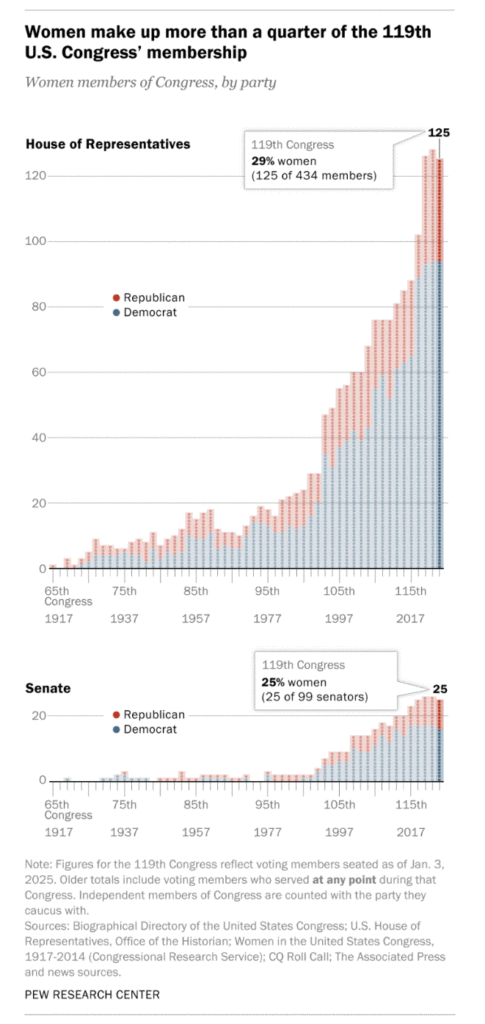
The changing face of Congress in 7 charts
Effectiveness of Physical Activity Interventions on Acute Inpatient Mental Health Units on Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review
Pinning down state authenticity: defining and validating a state authenticity measure
Global, regional, and national burden of household air pollution, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Impact of survey item wording on reported tobacco use among youth: effect of adding ‘even one or two puffs’ to use questions
The state of academic freedom worldwide
The decline in intentions to stop watching pornography among young adults
The Eugenic Origins of Three Strikes Laws: How “Habitual Offender” Sentencing Laws Were Used as a Means of Sterilization

“Habitual offender” laws first spread across the country in the early 1900s as part of the eugenics movement, which grew in the 1880s and reached its peak in the 1920s. The aim of the eugenics movement was to create a superior race in order to address social problems such as crime and disease, which the movement assumed had a biological basis.3 Applying pseudoscience, laws and policies were created to prevent those who were deemed inferior, such as the mentally ill, those convicted of criminal offenses, or the physically frail, from reproducing. Eugenics and racism are deeply entwined, and the “projects” of eugenics supported “racial nationalism and racial purity.”4 One example of the relationship between race and eugenics is found in Nazi Germany, where “Nazi planners appropriated and incorporated eugenics as they implemented racial policy and genocide.”5
Medical vs Nonmedical Cannabis Use Among US Adults
Global, regional, and national burden of suicide, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Returning PhD graduates: Maneuvering research productivity, identity, and institutional culture
Barriers to health, social and long-term care access among older adults: a systematic review of reviews
Racially minoritized patients can benefit from racially concordant providers but struggle to find them
State of the Global Climate 2024

Models of promising practices on legal capacity and supported decision-making for people with disabilities
Views On Marriage and Love Following Sexual Harassment Experiences: A Moderated Mediation Analysis
Parent-adolescent sexual and reproductive health information communication in Ghana
Interview with Alex Keuroghlian on responding to policy threats to protections for transgender and nonbinary people

Turning surplus food into millions of meals
