
Participant observers: Anthropology, colonial development, and the reinvention of society in Britain

news, new scholarship & more from around the world




Journal of Planning History, Ahead of Print.
Around 1970, the City of Berkeley briefly became an epicenter of radical experimentation in urban planning and design, directly stemming from the counterculture of the late 1960s. This essay examines the ideological and political emergence of Berkeley’s counterculture urbanism, arguing that its experiments left two important legacies in the history of planning. On the level of utopian thought, it articulated a clear alternative to mainstream capitalist urban development, or what Henri Lefebvre called “abstract space.” On the level of contemporary planning practices, it opened up still-unresolved conflicts, especially between localized environmental preservation and the abstract, economic demands for affordable housing.



A detail from the Standard of Ur, from third-millennium B.C. Sumeria, shows prisoners of war between soldiers.








Slum photography was at the heart of progressive campaigns against urban poverty. And it was a weapon against poor people.





The convergence of dance art and therapeutic culture engendered the development of dance-movement therapy in the mid to late 20th century internationally. This article traces the sociopolitical, institutional, and aesthetic influences that coalesced in this process by contrasting histories of dance-movement therapy in Hungary and in the United States. The professionalization dance-movement therapy, through which it established its own theory, practice, and training institutions, occurred first in the United States in the late 1940s. Modern dancers in the United States began to conceptualize their activity as therapeutic, and the dancer as a (secular) healer, a therapist. The influx of therapeutic concepts into the field of dance is viewed as an example of therapeutic discourse permeating various areas of life in the 20th century. The Hungarian case provides a contrasting history of therapeutic culture, one that deviates from the predominant view of the phenomenon as a product of the global spread of Western modernization and the growth of free-market capitalism. Hungarian movement and dance therapy indeed developed independently from its American predecessor. Its history is intimately tied to the sociopolitical context of state-socialist period, particularly to the institutionalization of psychotherapy in public hospitals, and to the adaptation of Western group psychotherapies within the informal setting of the “second public sphere.” The legacy of Michael Balint and the British object-relations school provided its theoretical framework. Its methodology was rooted in postmodern dance. The methodological differences between American dance-movement therapy and the Hungarian method reflects the shift in dance aesthetics that occurred internationally between 1940 and 1980s.

















Members of Young Americans for Freedom ride in a vehicle as they participate in the Loyalty Day Parade in Philadelphia, Pa., in 1966.

Jane Addams circa 1891
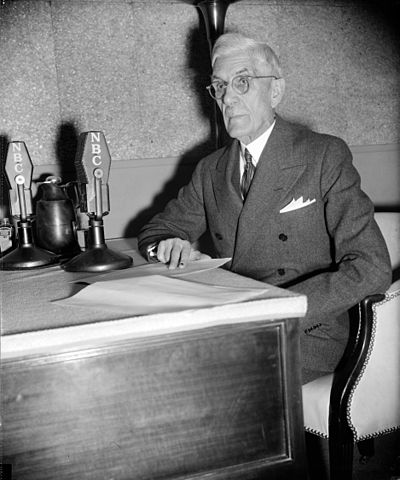







This research note discusses in some detail the economic problems with the very popular Old-Age Revolving Pension Plan (aka the Townsend Plan promoted and publicized by Dr. Francis E. Townsend (above)) of the 1930’s.

